C.elegans Made in SunyBiotech Contribute to Researchers Publishing a Hundred High-Quality Papers
2022-05-20 15:19
Founded in 2016, SunyBiotech Co., Ltd is committed to providing high-quality and efficient C. elegans gene editing services to prestigious university laboratories worldwide. Since our inception, SunyBiotech has registered the gene alleles Syb and PHX on CGC and Wormbase.
Since May 2017, SunyBiotech has undertaken C. elegans gene editing services. Our clients are spreading across Asia, Europe, North America, South America, and Oceania (see Figure 1). At present, 95 of the top 100 world-renowned universities in the QS Rankings are SunyBiotech clients.
Figure 1: Global distribution of SunyBiotech clients
Europe: Denmark, Finland, Czech Republic, Norway, Portugal, Poland, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands, Austria, Sweden, Switzerland, Spain, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom.
Asia: China, India, Singapore, Japan, South Korea, Israel, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and Turkey
North America: the United States, Canada, and Mexico
South America: Uruguay and Argentina
Oceania: Australia
Till May 1st, 2022, our clients have published nearly 100 papers (see appendix) using a total of 239 strains edited by SunyBiotech, which makes us quickly went from 0 to 100 in four short years (see Figure 2). Among the 100 papers, there are 55 with an impact factor of more than 5, and 25 have an impact factor of more than 10 (calculated according to the impact factor of the journal when the paper was published). It is worth mentioning that 5 of them were published in the top journals of "NCS", including 4 in Nature and 1 in Cell.
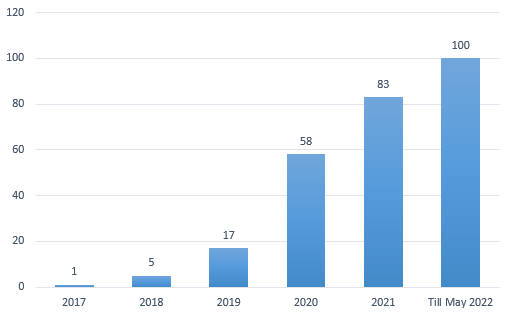
Figure 2: Cumulative number of papers using C.elegans made in SunyBiotech
In the past four years, “SunyBiotech C.elegans” has frequently appeared in world-renowned academic journals.
In October 2017, on the first anniversary of our establishment, the strain edited by SunyBiotech was published for the first time. Lionel Pintard (PI) published a paper entitled “Channel Nucleoporins Recruit PLK-1 to Nuclear Pore Complexes to Direct Nuclear Envelope Breakdown in C. elegans” in the well-known academic journal Developmental Cell, in which the strain PHX207 npp-1(syb207)IV was used.
In June 2019, “SunyBiotech C.elegans” was firstly listed on the top journal. Oded Rechavi (PI) published a paper in Cell entitled “Neuronal Small RNAs Control Behavior Transgenerationally” using two of our strains PHX776 rde-4(ne299);saeg-2(syb776) / PHX777 rde-4(ne299);saeg-2(syb777). In October of the same year, PHX1028 cup-5(syb1028)III was used in the paper “A secreted microRNA disrupts autophagy in distinct tissues of Caenorhabditis elegans upon ageing” published in Nature Communications by Shen Yidong (PI) from Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, which is the first time that “SunyBiotech C.elegans” has been used and published by Chinese scientists.
In March 2020, “SunyBiotech C.elegans” first appeared on Nature. Jerome Goudeau team published a paper entitled “Addendum: A lysosomal switch triggers proteostasis renewal in the immortal C. elegans germ lineage” using our strain PHX798 gld-1(syb798). In August of the same year, Oliver Hobert (PI) published a paper in Nature entitled “Unique homeobox codes delineate all the neuron classes of C. elegans” using up to 14 strains of “SunyBiotech C.elegans”, which also sets a record for the number of strains edited by SunyBiotech in a single paper.
After several years of accumulation, SunyBiotech has become a well-known brand recognized by the academic field of C.elegans. The quantity and quality of papers published by clients using “SunyBiotech C.elegans” has increased year by year. In 2020, the number of publications showed an explosive growth, reaching 41 papers. The good momentum still continues in 2022. In the first 4 months, the number of publications has reached the number of that in the whole year of 2019.
We believe that in the future, “SunyBiotech C.elegans” will provide a good experiment model for more researchers, reveal more scientific secrets hidden in C. elegans, and make greater contributions to the cause of life science.
We also sincerely thank every valued client of SunyBiotech. It is with your trust, support and dedication that so many high-level and high-quality academic papers have come out, and also inspire us to provide more refined and better services for every researcher who is committed to scientific research. We will continue to forge ahead towards the mission of “serve life science, benefit human beings”.
If you would like to get more information or services about SunyBiotech, please log on to our official website (https://www.sunybiotech.com/) or contact us at service@sunybiotech.com.
Appendix: Papers using “SunyBiotech C.elegans”
Paper Title | Journal Name |
Channel Nucleoporins Recruit PLK-1 to Nuclear Pore Complexes to Direct Nuclear Envelope Breakdown in C. elegans | Developmental Cell |
Membrane Fluidity Is Regulated Cell Nonautonomously by Caenorhabditis elegans PAQR-2 and Its Mammalian Homolog AdipoR2 | Genetics |
Function and regulation of the Caenorhabditis elegans Rab32 family member GLO-1 in lysosome-related organelle biogenesis | PLOS Genetics |
Chromatin Modifiers SET-25 and SET-32 Are Required for Establishment but Not Long-Term Maintenance of Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance | Cell Reports |
BUB-1 promotes amphitelic chromosome biorientation via multiple activities at the kinetochore | eLife |
Neuronal Small RNAs Control Behavior Transgenerationally | Cell |
A secreted microRNA disrupts autophagy in distinct tissues of Caenorhabditis elegans upon ageing | Nature Communications |
A fln-2 mutation affects lethal pathology and lifespan in C. elegans | Nature Communications |
PCMD-1 Organizes Centrosome Matrix Assembly in C. elegans | Current Biology |
Redox-dependent and redox-independent functions of Caenorhabditis elegans thioredoxin | Redox Biology |
A developmental gene regulatory network for C elegans anchor cell invasion | Development |
Heme peroxidase HPX-2 protects Caenorhabditis elegans from pathogens | PLOS Genetics |
An autism-causing calcium channel variant functions with selective autophagy to alter axon targeting and behavior | PLOS Genetics |
Sumoylation regulates protein dynamics during meiotic chromosome segregation in C. elegans oocytes | Journal of Cell Sicence |
Single-strand annealing mediates the conservative repair of double-strand DNA breaks in homologous recombination-defective germ cells of Caenorhabditis elegans | DNA Repair |
ALG-2/AGO-Dependent mir-35 Family Regulates DNADamage-Induced Apoptosis Through MPK-1/ERK MAPK Signaling Downstream of the Core Apoptotic Machinery in Caenorhabditis elegans | Genetics |
ASNA-1 oxidation induced by cisplatin exposure enhances its cytotoxicity by selectively perturbing tail anchored protein targeting | bioRxiv |
Microtubule Assembly and Pole Coalescence: Early Steps in C. elegans Oocyte Meiosis I Spindle Assembly | Biologist |
Split-wrmScarlet and split-sfGFP: tools for faster, easier fluorescent labeling of endogenous proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans | BioRxiv |
PCMD-1 bridges the centrioles and the PCM scaffold in C. elegans | biorxiv |
Paper Title | Journal Name |
The evolutionarily conserved ESRE stress response network is activated by ROS and mitochondrial damage | BMC Biology |
Analysis of m6A RNA methylation in Caenorhabditiselegans | Cell Discovery |
Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Promotes Sleep through a Combined Series and Parallel Neural Circuit | Current Biology |
Temporal, Spatial, Sexual and Environmental Regulation of the Master Regulator of Sexual Differentiation in C. elegans | Current Biology |
Innate Immunity Promotes Sleep through Epidermal Antimicrobial Peptides | Current Biology |
Establishment and maintenance of motor neuron identity via temporal modularity in terminal selector function | eLife |
A conserved cysteine‐based redox mechanism sustains TFEB/HLH‐30 activity under persistent stress | EMBO Journal |
SLC17A6/7/8 Vesicular Glutamate Transporter Homologs in Nematodes | Genetics |
A Region of UNC-89 (Obscurin) Lying between Two Protein Kinase Domains Is a Highly Elastic Spring Required for Proper Sarcomere Organization | Journal of Molecular Biology |
Unique homeobox codes delineate all the neuron classes of C. elegans | Nature |
Epidermal control of axonal attachment via β-spectrin and the GTPase-activating protein TBC-10 prevents axonal degeneration | Nature Communications |
Cysteine synthases CYSL-1 and CYSL-2 mediate C. elegans heritable adaptation to P. vranovensis infection of cysteine synthases in progeny | Nature Communications |
MALT-1 mediates IL-17 neural signaling to regulate C. elegans behavior, immunity and longevity | Nature Communications |
The Rho-GEF PIX-1 directs assembly or stability of lateral attachment structures between muscle cells | Nature Communications |
A wake-active locomotion circuit depolarizes a sleep-active neuron to switch on sleep | PLOS Biology |
Roles for the RNA polymerase III regulator MAFR-1 in regulating sperm quality in Caenorhabditis elegans | Scientific Reports |
The TRPV Channel OSM-9 is Required for Sleep-Dependent Olfactory Memory and is Expressed in Sensory Neurons That Do Not Promote Butanone Attraction | bioRxiv |
A caveolin binding motif in Na/K-ATPase is required for stem cell differentiation and organogenesis in mammals and C. elegans | Science Advances |
Modulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress response attenuates neurodegeneration in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of spinal muscular atrophy | Dis Model Mech |
The Caenorhabditis elegans CUB-like-domain containing protein RBT-1 functions as a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry6Aa toxin | PLOS PATHOGENS |
Paper Title | Journal Name |
Addendum: A lysosomal switch triggers proteostasis renewal in the immortal C. elegans germ lineage | Nature |
An ABCG Transporter Functions in Rab Localization and Lysosome-Related Organelle Biogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans | Genetics |
Regulation of sleep by KIN-29 is not developmental | microPublication Biology |
ceh-84, an unusual homeobox gene | microPublication Biology |
Inhibition of the oligosaccharyl transferase in Caenorhabditis elegans that compromises ER proteostasis suppresses p38-dependent protection against pathogenic bacteria | PLOS Genetics |
Ancestral function of Inhibitors-of-kappaB regulates Caenorhabditis elegans development | Scientific Reports |
Alleviating chronic ER stress by p38-Ire1-Xbp1 pathway and insulin-associated autophagy in C. elegans neurons | PLOS Genetics |
A Natural Mutational Event Uncovers a Life History Trade-Off via Hormonal Pleiotropy | Current Biology |
Leveraging a gain-of-function allele of Caenorhabditis elegans paqr-1 to elucidate membrane homeostasis by PAQR proteins | PLOS Biology |
The Caenorhabditis elegans homolog of human copper chaperone Atox1, CUC-1, aids in distal tip cell migration | BioMetals |
Host Mucin Is Exploited by Pseudomonas aeruginosa To Provide Monosaccharides Required for a Successful Infection | mBio |
Alternative splicing of coq-2 controls the levels of rhodoquinone in animals | eLife |
Alternative splicing of COQ-2 determines the choice between ubiquinone and rhodoquinone biosynthesis in helminths | BioRxiv |
An omics analysis of genetic sleep loss in C. elegans | eDiss |
A Mitochondrial Stress-Specific Form of HSF1 Protects against Age-Related Proteostasis Collapse | Developmental Cell |
Tissue-specific isoforms of the single C. elegans Ryanodine receptor gene unc-68 control specific functions | PLOS Biology |
Temporal transitions in post-mitotic neurons throughout the C. elegans nervous system | BioRxiv |
Characterization of two Caenorhabditis elegans Orthologs of Selenium-binding protein 1, associated with aging | dbt |
Split-wrmScarlet and split-sfGFP: tools for faster, easier fluorescent labeling of endogenous proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans | Genetics |
A nervous system-specific subnuclear organelle in Caenorhabditis elegans | Genetics |
Paper Title | Journal Name |
Telomeric double-strand DNA-binding proteins DTN-1 and DTN-2 ensure germline immortality in Caenorhabditis elegans | eLife |
Cortical recruitment of centralspindlin and RhoA effectors during meiosis I of Caenorhabditiselegans primary spermatocytes | Journal of Cell Sicence |
Interactions between the WEE-1.3 kinase and the PAM-1 aminopeptidase in oocyte maturation and the early C. elegans embryo | G3-Genes Genomes Genetics |
The decrease of intraflagellar transport impairs sensory perception and metabolism in ageing | Nature Communications |
A collection of toolkit strains reveals distinct localization and dynamics of membrane-associated transcripts in epithelia | Cell Reports |
Rewiring of the ubiquitinated proteome determines ageing in C. elegans | Nature |
Gene bookmarking by the heat shock transcription factor programs the insulin-like signaling pathway | Molecular Cell |
A C. elegans model of C9orf72-associated ALS/FTD uncovers a conserved role for eIF2D in RAN translation | Nature Communications |
PDZD-8 and TEX-2 regulate endosomal PI(4,5)P2 homeostasis via lipid transport to promote embryogenesis in C. elegans | Nature Communications |
Identification of Novel Therapeutic Targets for Polyglutamine Diseases That Target Mitochondrial Fragmentation | MDPI |
MON-2, a Golgi protein, mediates autophagy-dependent longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans | Science Advances |
The LRR-TM protein PAN-1 interacts with MYRF to promote its nuclear translocation in synaptic remodeling | eLife |
Alternative somatic and germline gene-regulatory strategies during starvation-induced developmental arrest | bioRxiv |
Spliceosomal component PRP-40 is a central regulator of microexon splicing | Cell Reports |
Combinatorial Assembly of Modular Glucosides via Carboxylesterases Regulates C. elegans Starvation Survival | Journal of the American Chemical Society |
INPP5K and Atlastin-1 maintain the nonuniform distribution of ER–plasma membrane contacts in neurons | Life Science Alliance |
Temporal transitions in the post-mitotic nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans | Nature |
Neuropeptide signalling shapes feeding and reproductive behaviours in male C. elegans | BioRxiv |
Signaling via the FLP-14/FRPR-19 neuropeptide pathway sustains nociceptive response to repeated noxious stimuli in C. elegans | Plos Genetics |
TIMELESS-TIPIN and UBXN-3 promote replisome disassembly during DNA replication termination in Caenorhabditis elegans | EMBO Journal |
Paper Title | Journal Name |
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Mediates Adiponectin Receptor Signaling Essential For Lipid Homeostasis and Embryogenesis | bioRxiv |
The anterior Hox gene ceh-13 and elt-1/GATA activate the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3 to specify posterior lineages in the C. elegans embryo | BioRxiv |
Neuronal SKN-1B modulates nutritional signalling pathways and mitochondrial networks to control satiety | Plos Genetics |
Overactivation of a sleep-active neuron decouples survival from the need to sleep | bioRxiv |
An Optogenetic Arrhythmia Model—Insertion of Several Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Mutations Into Caenorhabditis elegans UNC-68 Disturbs Calstabin-Mediated Stabilization of the Ryanodine Receptor Homolog | Frontiers in Physiology |
Loss of circRNAs from the crh-1 gene extends the mean lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans | Aging Cell |
Neuron-epidermal attachment protects hyper_x005f fragile axons from mechanical strain | Cell Reports |
Robust regulatory architecture of pan-neuronal gene expression | Current Biology |
SEMO-1, a novel methanethiol oxidase in Caenorhabditis elegans, is a pro-aging factor conferring selective stress resistance | BioFactors |
Robust regulatory architecture of pan-neuronal gene expression | Current Biology |
Neuron-epidermal attachment protects hyper_x005f fragile axons from mechanical strain | Cell Reports |
Allosteric regulation of C. elegans AMP-activated protein kinase | microPublication Biology |
Characterization of N- and C-terminal endogenously tagged Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 2 (TDPT-1) C. elegans strains | microPublication Biology |
Genetic analysis of daf-18/PTEN missense mutants for starvation resistance and developmental regulation during Caenorhabditis elegans L1 arrest | G3-Genes Genomes Genetics |
A novel de novo FEM1C variant as a potential cause of neurodevelopmental disorder with absent speech, pyramidal signs, and limb ataxia | bioRxiv |
The anterior Hox gene ceh-13 and elt-1/GATA activate the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3 to specify posterior lineages in the C. elegans embryo | PLOS Genetics |
Cortical microtubule pulling forces contribute to the union of the parental genomes in the Caenorhabditis elegans zygote | eLife |
Sensory neuron transcriptomes reveal complex neuron-specific function and regulation of mec-2/Stomatin splicing | Oxford Academic |
Sleep neuron depolarization promotes protective gene expression changes and FOXO activation | Current Biology |
C. elegans Sine oculis/SIX-type homeobox genes act as homeotic switches to define neuronal subtype identities | bioRxiv |




