The Neuropeptidergic Connectome of Caenorhabditis elegans: Unlocking the Secrets of Neural Communication
2025-04-24 15:37
Keywords: neuropeptidergic connectome, neuromodulatory signaling, neuronal connectivity, neurosecretory center, GPCRs
Introduction
In the field of biology, Caenorhabditis elegans (C.elegans) has become a “star organism” for scientists studying neuroscience due to its simple yet exquisite nervous system. For a long time, scientists have been committed to mapping synaptic wiring diagrams, or connectomes to explore the neural basis of brain function. However, chemical synapses are just one type of important neuronal connection. Neuropeptides, as a class of important signaling molecules, play a key role in regulating neural activity and behavior through their unique “wireless” signaling mode. Although neuropeptide signaling is widespread in the nervous system, previous connectome studies have mainly focused on synaptic wiring diagrams, and the understanding of neuropeptide signaling networks has been relatively limited. An article published in the journal Neuron has filled this research gap, providing us with a comprehensive and detailed map of the neuropeptide signaling network.
Contribution of SunyBiotech:
SunyBiotech constructed many key C. elegans strains for this article, laying the foundation for the comprehensive maping of the neuropeptide signaling network and functional research:
flp-1(syb2658[flp-1::T2A::3XNLS::GFP]) IV
flp-14(syb3323[flp-14::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) III
nlp-13(syb3411[nlp-13::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) V
nlp-58(syb3191 [nlp-58::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) V
nlp-45(ot1032[nlp-45::T2A::GFP::H2B]) X
flp-26(syb3588[flp-26::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) X
ins-9(syb2616[ins-9::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) X
ins-9(syb5536[ins-9::SL2::gfp::H2B]) X
flp-28(syb3207[flp-28::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) X
flp-3(syb2634[flp-3::T2A::3XNLS::GFP]) X
ins-6(syb2685[ins-6::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) II
ins-6(syb5463[ins-6::SL2::GFP::H2B]) II;otIs669 him-5(e1490) V
nlp-50(syb2704[nlp-50::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) II
flp-20 (syb3241 [flp-20::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) X
flp-20(syb4049[flp-20::SL2::GFP::H2B]) X
nlp-51(syb2805 [nlp-51::T2A::3xNLS::GFP]) II
nlp-51(syb3936[nlp-51::SL2::GFP::H2B]) II
trh-1(syb4421[trh-1::SL2::GFP::H2B]) IV
flp-5(syb4513[flp-5::SL2::GFP::H2B]) X
flp-32 (T2A::3xNLS::GFP)
flp-32(syb4374[flp-32::SL2::gfp::H2B]) X
flp-27 (T2A::3xNLS::GFP)
flp-27(syb4413 [flp-27::SL2::GFP::H2B]) II
npr-37(syb4440[npr-37::SL2::GFP::H2B]) IV
dmsr-2(syb4514 [dmsr-2::SL2::gfp::H2B]) I
dmsr-6 (syb4442 [dmsr-6::SL2::GFP::H2B]) I
npr-32 (syb4433 [npr-32::SL2::GFP::H2B] IV
aex-2(syb4447 [aex-2::SL2::GFP::H2B)] X
trhr-1(syb4453[trhr-1::SL2::GFP::H2B]) I
trk-1 (SL2::GFP::H2B)
frpr-19(syb4523[frpr19::SL2::GFP::H2B]) IV
nmur-2(syb4517 [nmur-2::SL2::GFP::H2B)] II
1. Construction of the Neuropeptidergic Connectome
Neuropeptide signaling involves the interaction of neuropeptides with specific G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). This mode of signal transduction is highly specific and can achieve long-distance communication between cells. The research team successfully constructed a draft of the neuropeptide signaling connectome in the nervous system of C. elegans by integrating single-cell anatomy, gene expression datasets, and biochemical analysis of receptor-ligand interactions. This process involved a comprehensive analysis of neuropeptide-GPCR interaction data, nervous system anatomy, and single-neuron expression data (Fig.1A and 1B). By using single-copy knockout reporter genes, researchers also assessed gene expression thresholds (Fig.1C), further refining the construction of the connectome and providing a basis for revealing the characteristics of the neuropeptide signaling network.
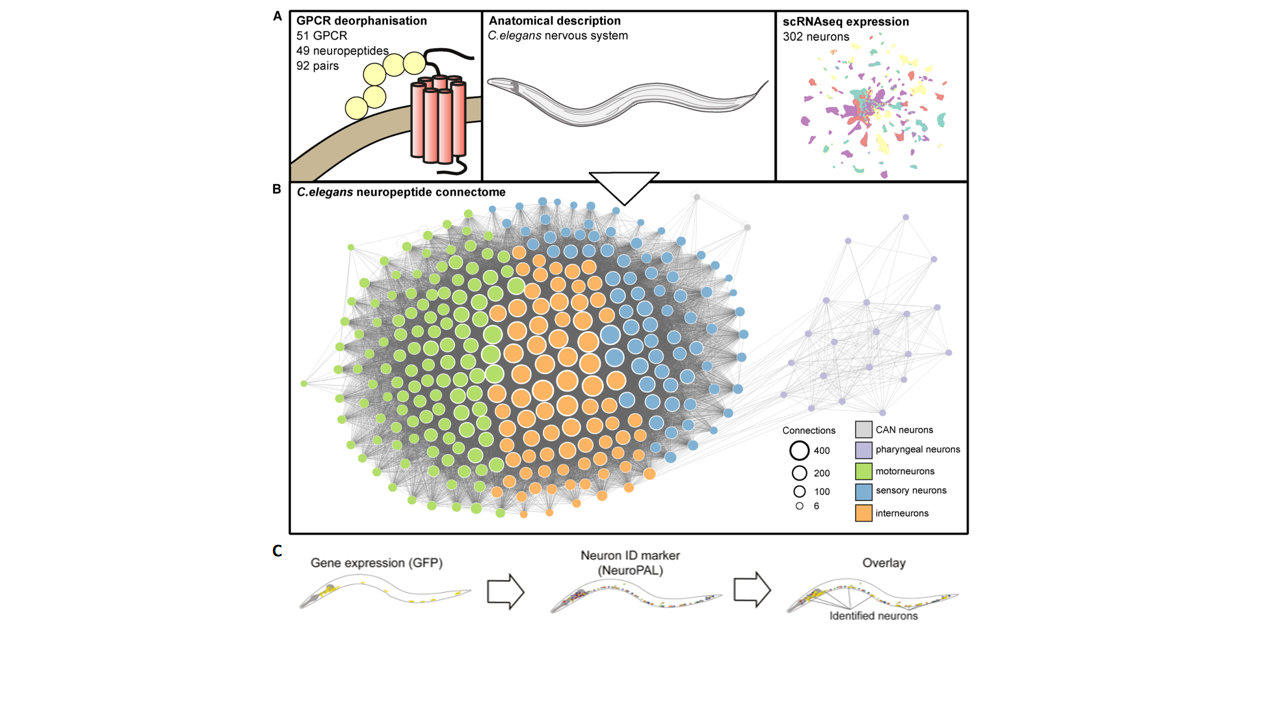
Figure 1. Construction of the Neuropeptidergic Connectome
2. High Density and Complex Network Features
The constructed neuropeptidergic connectome exhibits high connection density, extended signaling cascades, autocrine foci (meaning neurons can influence themselves via neuropeptide release), and a dispersed topological structure (Fig.2A-2C). It was found that the core part is a large, highly interconnected area, containing three constituent communities (sensory core, hub neurons, and motor core), which share similar input connection patterns (Fig.2D). This complex network structure allows neuropeptide signaling to spread widely in the nervous system and has high flexibility and adaptability.
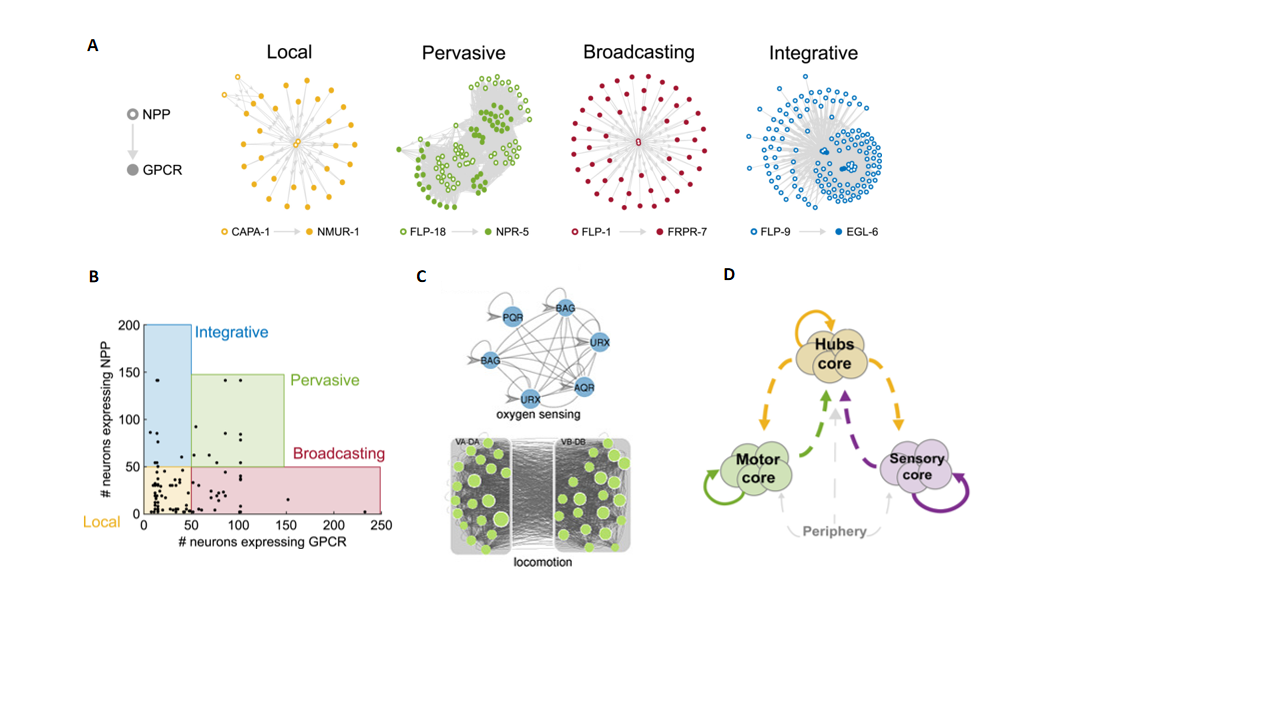
Figure 2. High Density and Complex Network Features
3. Overlooked Neuromodulatory Hubs
Some key hubs in the neuropeptide network are composed of neurons that have rarely been studied. For example, AVKL/R, PVQL/R, and PVR, these hub neurons have a high degree of connectivity in the neuropeptide signaling network, but their synaptic connections are relatively few (Fig. 3), indicating that they may widely regulate downstream circuits by releasing large amounts of neuropeptides. This finding suggests that there may be many neuromodulatory mechanisms in the nervous system that have not been fully recognized, and these mechanisms play an important role in the overall function of the nervous system.
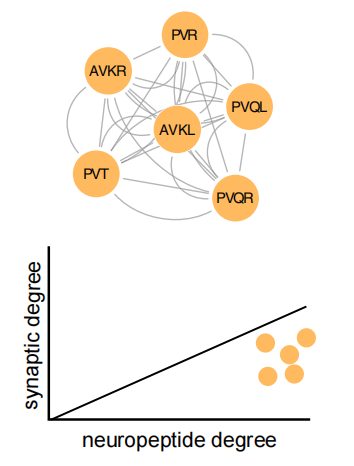
Figure 3. Identified neuropeptidergic hub neurons
Conclusion
The neuropeptidergic connectome of C. elegans provides a prototype for understanding the organization of neuralmodulatory signaling networks. In-depth studies of the neuropeptide signaling network in this model organism can lay the foundation for exploring similar mechanisms in more complex organisms, including humans. This not only helps to unravel the complexity of brain function but may also offer new insights for clinical applications in neuroscience, such as the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. In summary, this article opens up an entirely new perspective, revealing the complex and exquisite “wireless” communication network constructed by neuropeptides in the nervous system.
References
Ripoll-Sánchez L, Watteyne J, Sun H, et al. The neuropeptidergic connectome of C. elegans. Neuron. 2023 Nov 15;111(22):3570-3589.e5.





